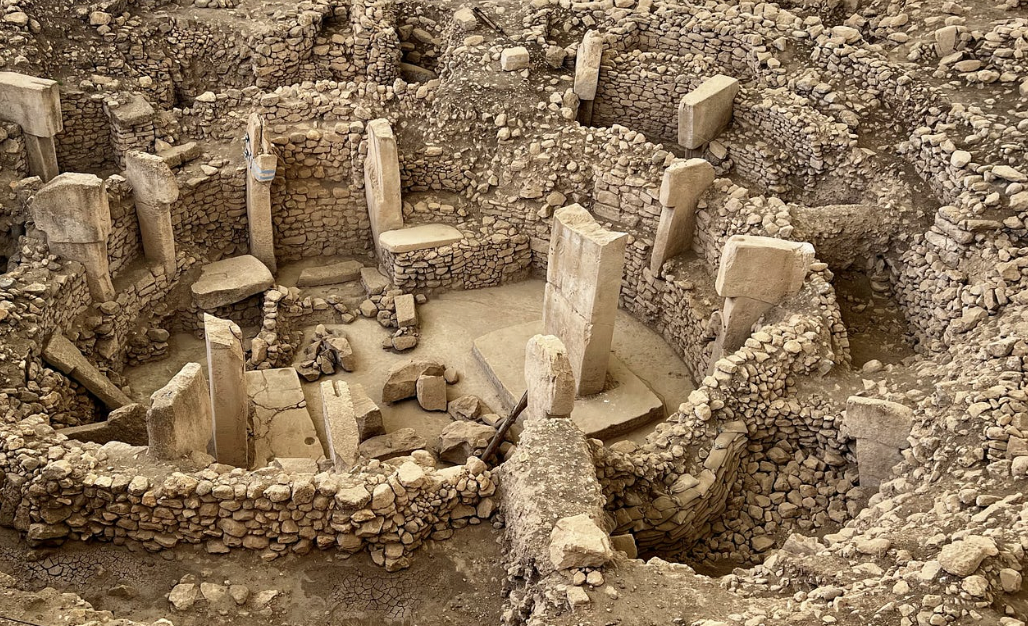
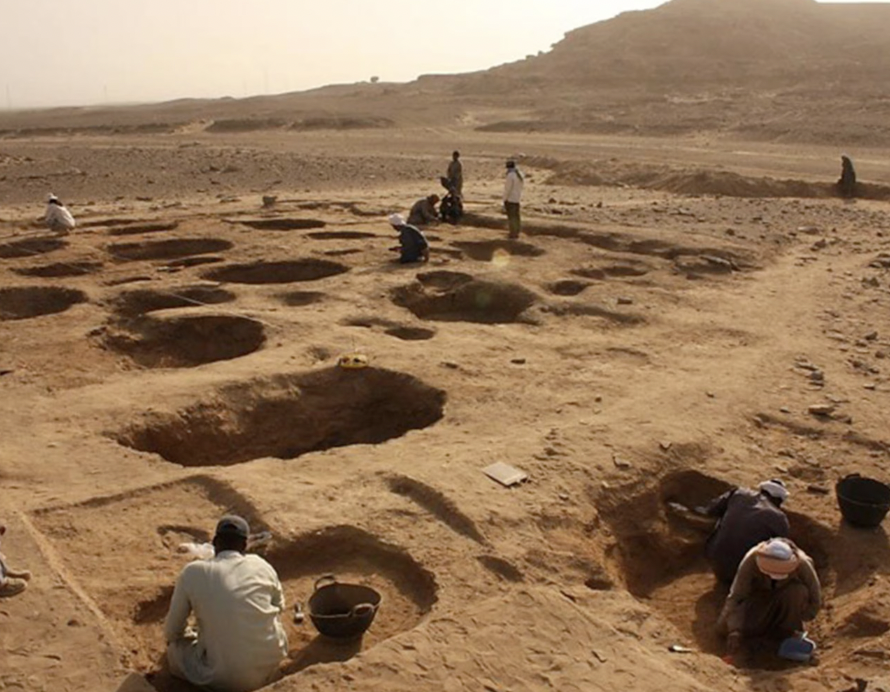
11 Archeological Finds That Challenge Our Understanding
It's amazing we know as much about our history as we do, but there is always more to learn.
Published 6 months ago in Wow
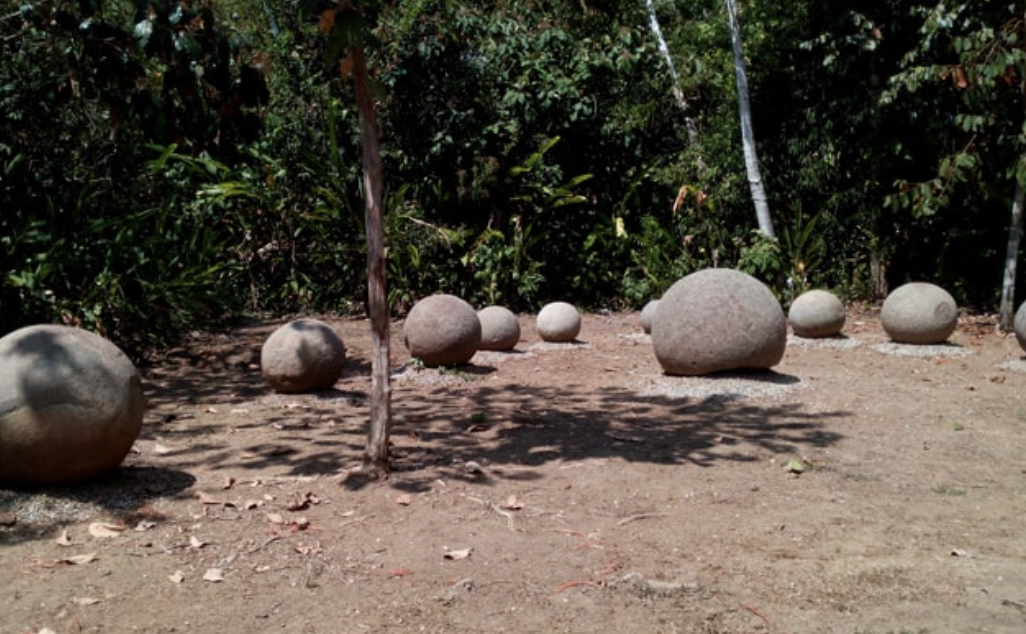
Archeologists are some of the most amazing scientists and detectives on the planet, solving the mystery of our history one dig site and artifact at a time. Considering they rely on discovering old things in the ground, it's incredible that we know as much about the history of our species as we do. But some things will always remain a mystery. These awesome 11 archeological finds changed the way we see our history, and made us rethink where, when, and how we were doing things in ancient times.
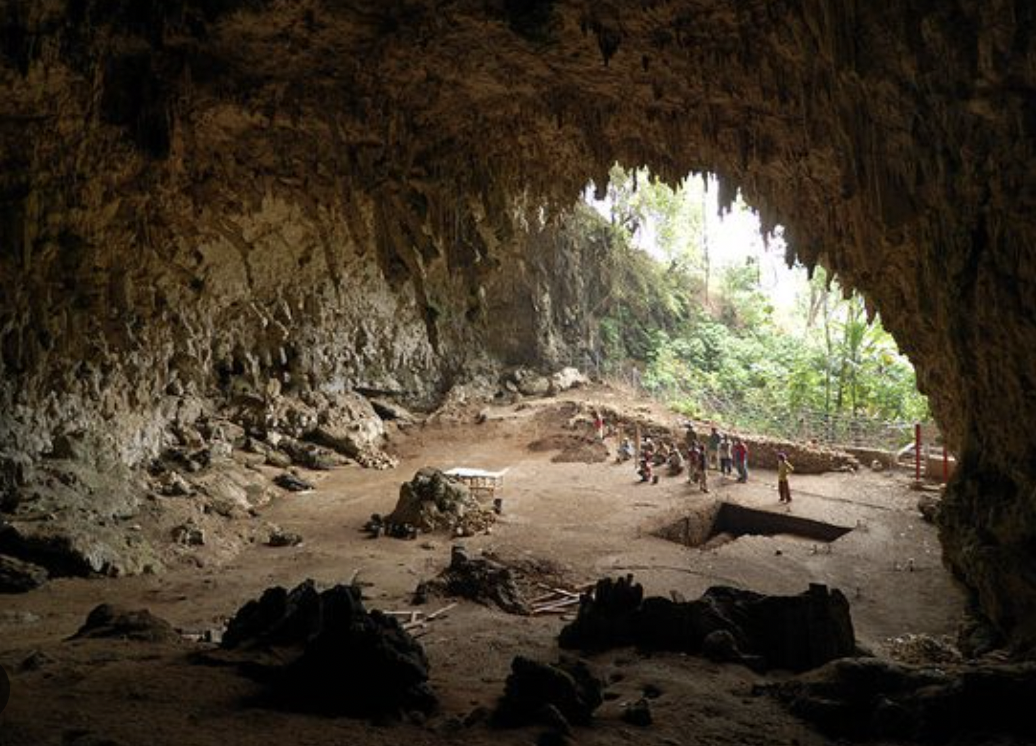
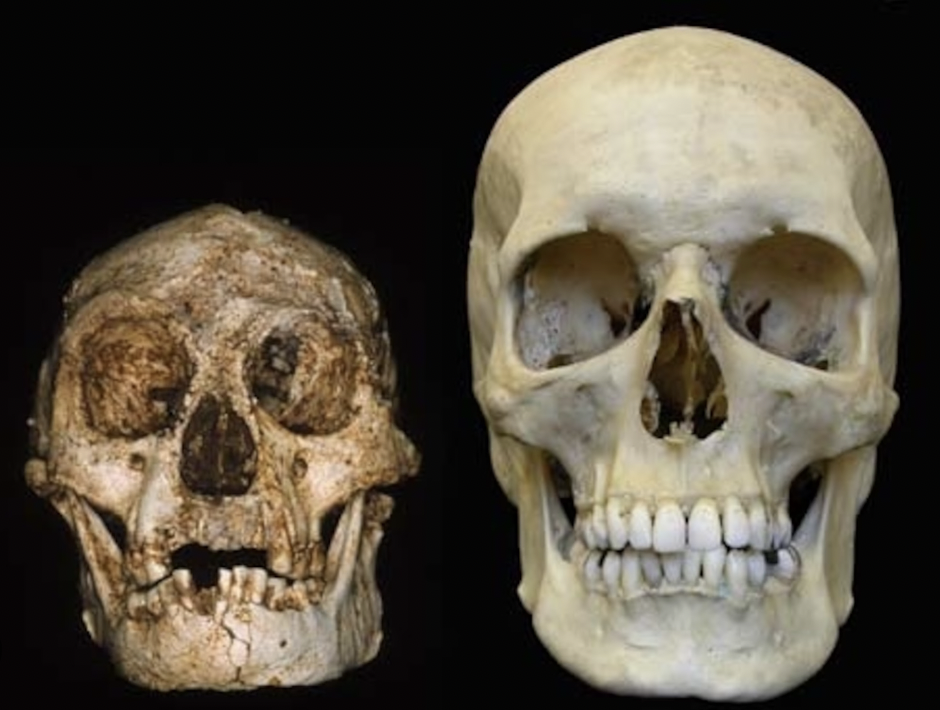
You probably know that humans as we think of ourselves today first evolved in Africa, and slowly migrated away around 60,000 years ago. Although there were other human-like species at the time, the people in that original group are the forefathers of 90% of modern humanity. However, one dig site in India is placing all of that into question.
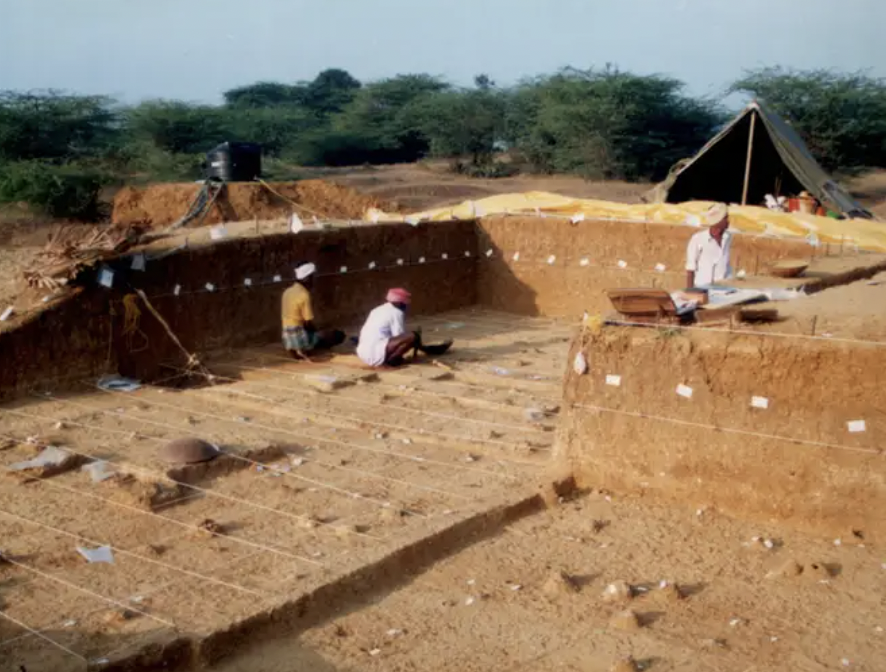
Advanced stone age tools were found and dated to be 200,000 years old, well before we would have arrived there. Either groups of humans developed and left Africa far before we thought they did, or a different stone age species was operating in India 200,000 years ago.
Read about that, and other archeological finds that make us question out past.
3
Advanced Stone-age Tools in India
We know that the majority of humans descended from people who left Africa around 60,000 years ago. But an under-studied site in India uncovered advanced stone age tools that are over 200,000 years old. How did that happen? Either some people left earlier than we thought, or a separate group developed those tools on their own.
8
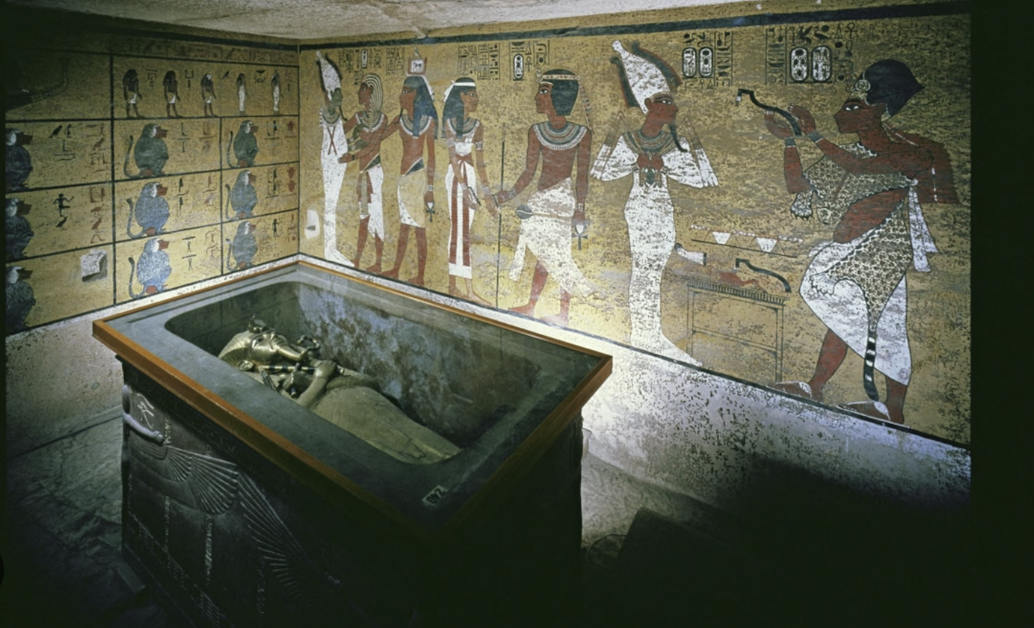
King Tut's Grave
The Egyptian boy pharaoh Tutankhamun is thought to have died unexpectedly. His resulting burial appears to be botched, with evidence that his mummy caught fire. With that in mind, some theorize that his tomb was originally built with others in mind, and that there is still more to discover in it.